Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Display?
- Types of Displays
- 3.1 Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD)
- 3.2 Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) Displays
- 3.3 Quantum Dot Displays
- 3.4 MicroLED Displays
- 3.5 Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Displays
- Display Resolutions
- Refresh Rate and Response Time
- Display Connectors
- Display Technologies for Specialized Applications
- 7.1 Touchscreen Displays
- 7.2 Curved Displays
- 7.3 High Dynamic Range (HDR) Displays
- 7.4 Gaming Displays
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on display technology! In this article, we will dive deep into the world of displays and explore the various types, resolutions, refresh rates, connectors, and specialized technologies that shape our visual experiences. Whether you are a technology enthusiast, a professional in the field, or simply curious about displays, this guide will provide you with valuable insights.
2. What is a Display?
A display, in the realm of computing, refers to a device that presents visual information generated by a computer or other electronic devices. It serves as the primary interface between users and their digital content, enabling us to consume information, view images and videos, play games, and perform various tasks. Displays are designed to render text, graphics, and multimedia content with clarity, color accuracy, and smoothness.
 |
| Display |
3. Types of Displays
The world of displays encompasses various technologies that have evolved over time to cater to different needs and preferences. Let's explore some of the prominent display technologies available today:
3.1 Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD)
LCDs are one of the most widely used display technologies. They consist of a layer of liquid crystals sandwiched between two polarizing filters. When an electric current passes through the liquid crystals, they align to allow or block light, thus creating the desired image. LCDs offer excellent color reproduction, wide viewing angles, and energy efficiency.
 |
| LCD Display Panel |
3.2 Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) Displays
OLED displays employ organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Unlike LCDs, OLED displays do not require a separate backlight, resulting in thinner and more flexible panels. OLEDs offer vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and deep black levels, as each pixel can be individually turned on or off.
 |
| OLED Technology |
3.3 Quantum Dot Displays
Quantum dot displays utilize semiconductor nanocrystals called quantum dots to enhance color reproduction. These tiny particles emit light at specific wavelengths when stimulated by an external light source. Quantum dot displays can achieve a wide color gamut, delivering more vibrant and accurate colors compared to traditional LCDs.
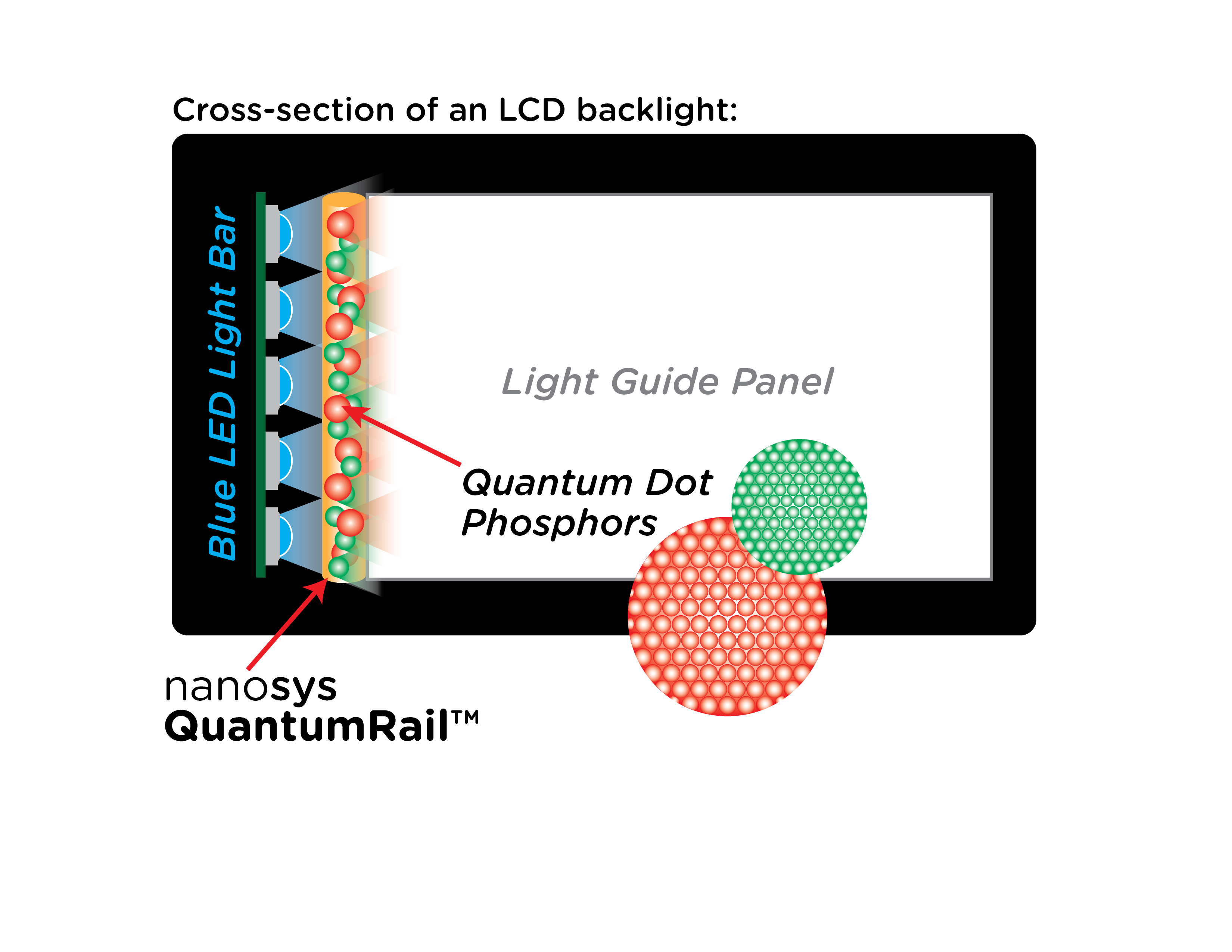 |
| Quantum Dot Display Technology |
3.4 MicroLED Displays
MicroLED displays represent the cutting edge of display technology. They consist of microscopic light-emitting diodes that individually emit light. MicroLEDs offer exceptional brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency. With their modular design, they can be assembled into large displays seamlessly.
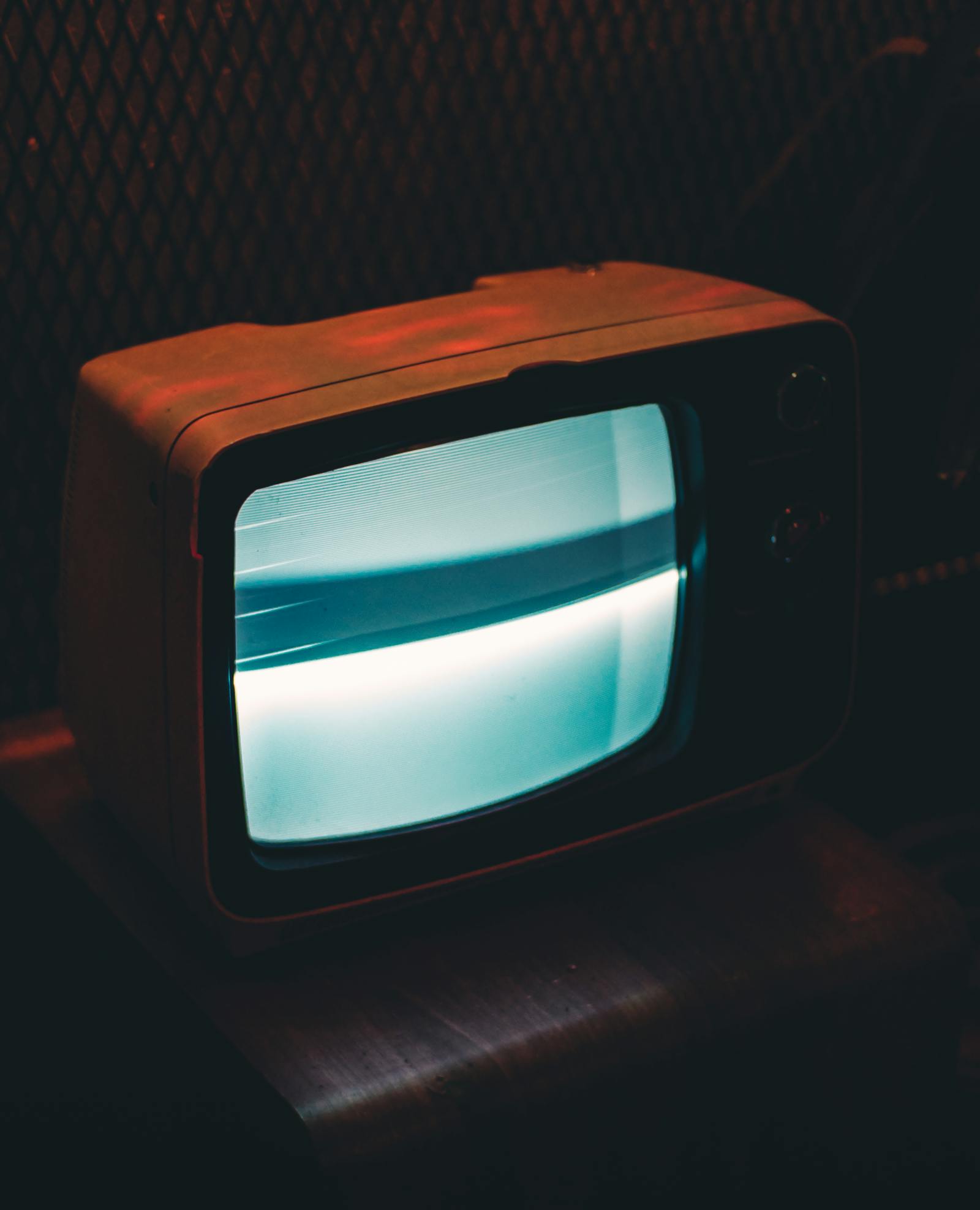
3.5 Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Displays
Cathode Ray Tube displays, or CRT displays, were once the dominant technology before the rise of flat panel displays. CRT displays use a cathode ray tube to generate images. They work by firing electrons from a cathode toward a phosphor-coated screen, creating images through the manipulation of electron beams. CRT displays were known for their deep blacks, high contrast ratios, and excellent color accuracy. However, due to their large size, weight, and power consumption, CRT displays have become extinct in recent years.
4. Display Resolutions
Display resolution refers to the number of pixels that make up the visual output of a display. Higher resolutions provide greater detail and sharper images. Here are some commonly used display resolutions:
- High Definition (HD): 1280x720 pixels
- Full High Definition (FHD): 1920x1080 pixels
- Quad High Definition (QHD): 2560x1440 pixels
- Ultra High Definition (UHD or 4K): 3840x2160 pixels
- 8K: 7680x4320 pixels
5. Refresh Rate and Response Time
The refresh rate of a display measures how many times per second the image on the screen is updated and is measured in Hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate results in smoother motion and reduces motion blur, enhancing the viewing experience, especially in fast-paced content and gaming.
Response time, on the other hand, measures how quickly a pixel can transition from one color to another. Lower response times minimize ghosting and ensure that images appear sharp and without artifacts.
6. Display Connectors
Display connectors serve as the interfaces that allow displays to connect with computers, gaming consoles, and other devices. Common display connectors include:
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
- DisplayPort
- VGA (Video Graphics Array)
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface)
- Thunderbolt
These connectors support different resolutions, refresh rates, and features, so it's crucial to ensure compatibility between your device and the display.
7. Display Technologies for Specialized Applications
In addition to the aforementioned display technologies, several specialized technologies cater to specific applications and user preferences. Let's explore some of them:
7.1 Touchscreen Displays
Touchscreen displays enable users to interact directly with the display by touching the screen. They utilize various technologies, including resistive, capacitive, and infrared, to detect touch inputs accurately. Touchscreens have become integral to smartphones, tablets, and other interactive devices.
7.2 Curved Displays
Curved displays offer an immersive viewing experience by matching the curvature of the human eye. They provide a wider field of view, reduce image distortion, and create a sense of depth. Curved displays are commonly found in gaming monitors and high-end televisions.
7.3 High Dynamic Range (HDR) Displays
High Dynamic Range (HDR) displays enhance the contrast and color accuracy of images, resulting in a more lifelike and visually stunning experience. HDR displays offer a broader range of luminosity and support a wider color gamut, reproducing details in both dark and bright areas more faithfully.
7.4 Gaming Displays
Gaming displays are specifically designed to meet the demands of avid gamers. They often feature high refresh rates, low response times, adaptive sync technologies (such as AMD FreeSync or NVIDIA G-Sync), and advanced color settings to provide smooth and immersive gaming experiences.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, this ultimate guide has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of display technology. We explored various display types, resolutions, refresh rates, connectors, and specialized technologies, including the historical significance of cathode ray tube (CRT) displays. By considering these factors, you can make informed decisions when choosing displays for your specific needs, whether it be for professional purposes, gaming, or everyday use. Stay updated with the latest advancements in display technology as it continues to evolve, enhancing our visual experiences. Should you have any further questions or require assistance, feel free to reach out to us. Happy exploring!